BitLocker keeps asking for recovery key at startup? After installing a Windows update which updates UEFI or TPM firmware, it may cause your computer to prompt for BitLocker recovery key on the first or second restart. In such situation, there is almost no other choice than to find your BitLocker recovery key.
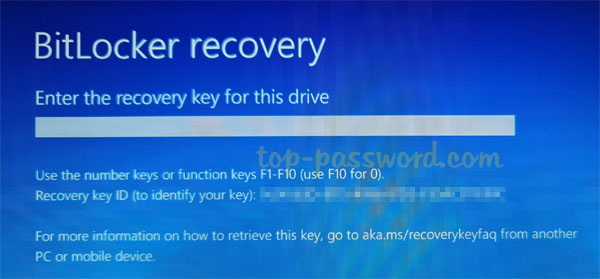
To save yourself a potential headache, you can prevent Windows update from asking for BitLocker recovery key upon reboot.
How to Prevent Windows Update from Asking for BitLocker Recovery Key
Before installing certain updates (such as KB5012170) which may cause BitLocker issue, you need to temporarily suspend BitLocker by following the below steps. It’s still not late if you’ve installed such update but have not yet restarted your computer.
- Open an elevated Command Prompt. Enter this command and press Enter to suspend BitLocker immediately. BitLocker will automatically resume after two reboots.
manage-bde -protectors -disable %systemdrive% -rebootcount 2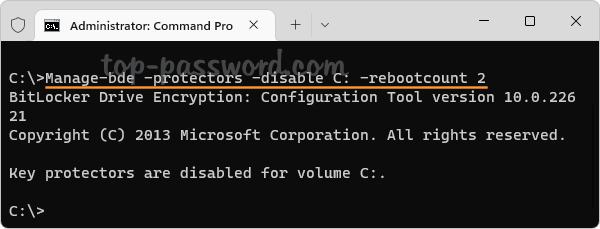
If you’re using Windows PowerShell (admin), enter this command instead:
Suspend-BitLocker -MountPoint "C:" -RebootCount 2 - Now, you can install Windows updates to update or flash the BIOS or TPM firmware on your computer, and it should never prompt you to enter BitLocker recovery key during boot. After a reboot, you can open an elevated Command Prompt and run this command to get the number of reboots remaining before automatically resuming BitLocker.
manage-bde -status %systemdrive%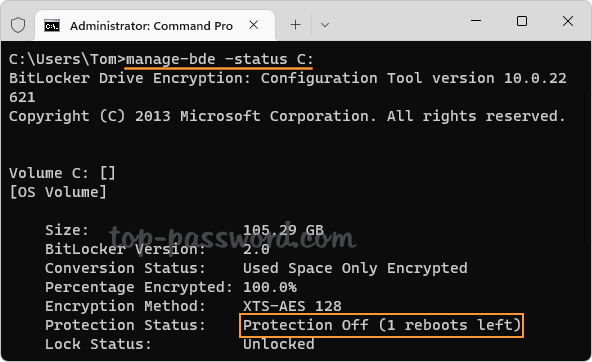
- After the second reboot, BitLocker should automatically be enabled and the protection status is On.
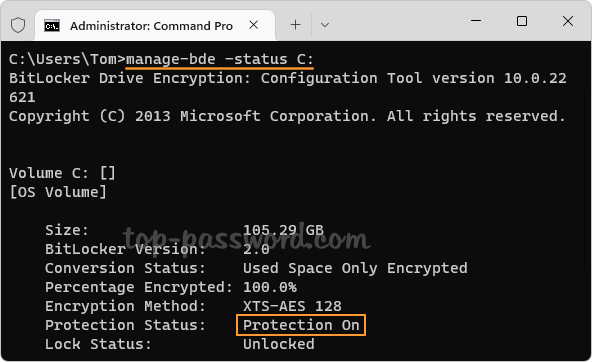
If you want to manually resume BitLocker to verify that it is enabled, use the following command:
manage-bde -protectors -enable %systemdrive%For Windows PowerShell, run this command:
Resume-BitLocker -MountPoint "C:"
That’s it!