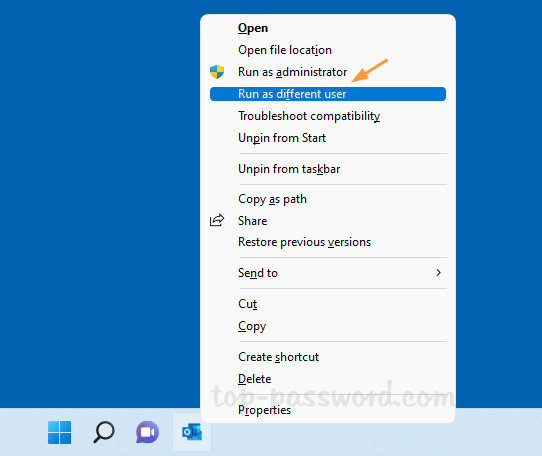
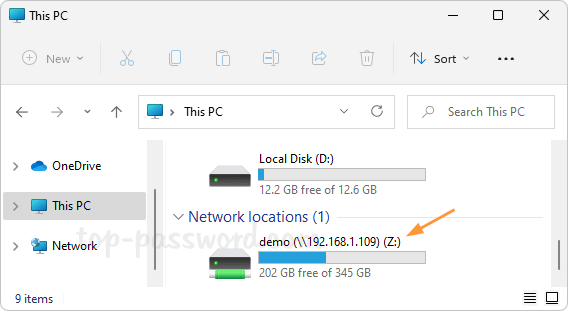
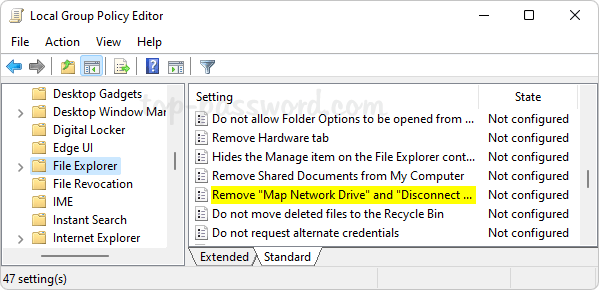
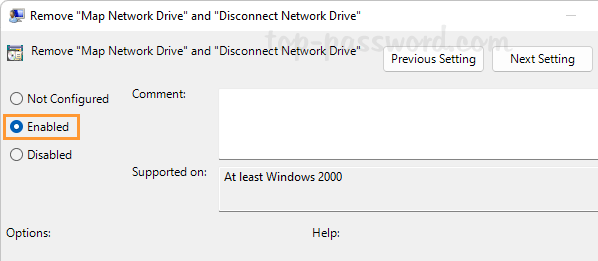
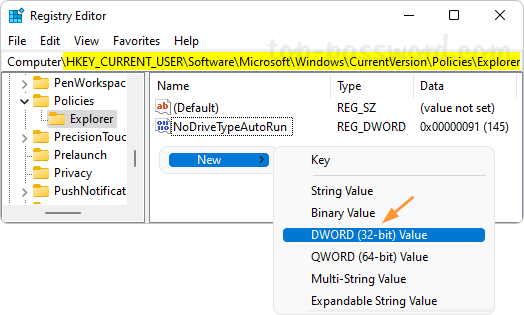
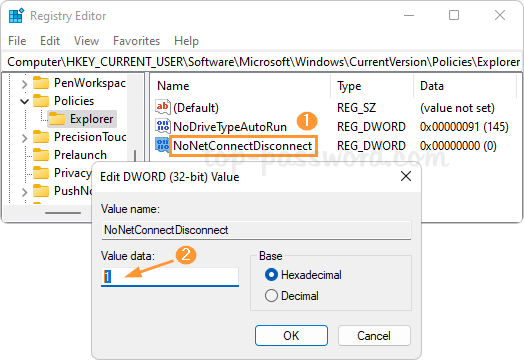
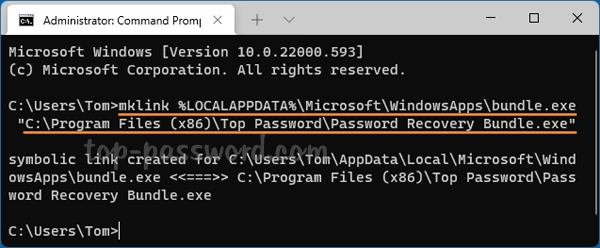
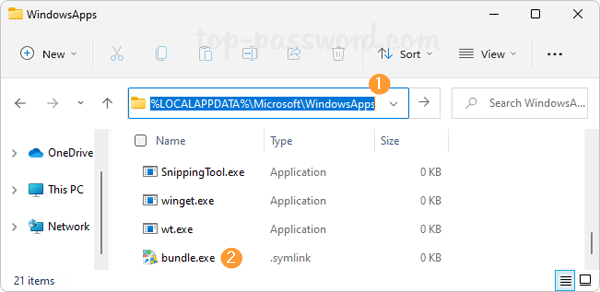
How do I forget a Wi-Fi network so the system doesn’t automatically connect to it? Can’t connect to the same wireless network after changing the Wi-Fi password on router? Removing previously saved Wi-Fi networks is often a helpful step to fix wireless connection problems. In this tutorial we’ll show you how to remove or forget a Wi-Fi network in just 3 steps on Windows 11.
How to Remove or Forget a Wi-Fi Network in Windows 11
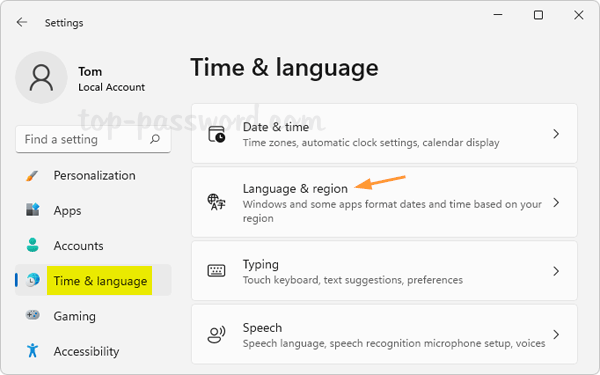
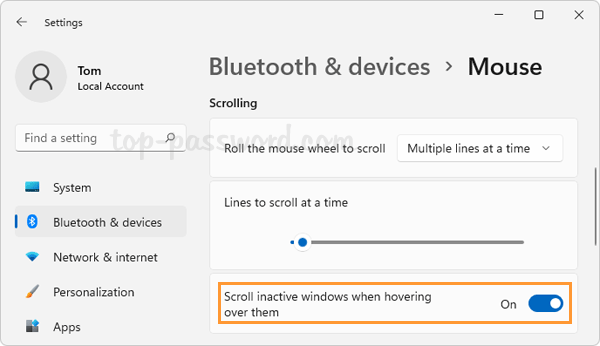
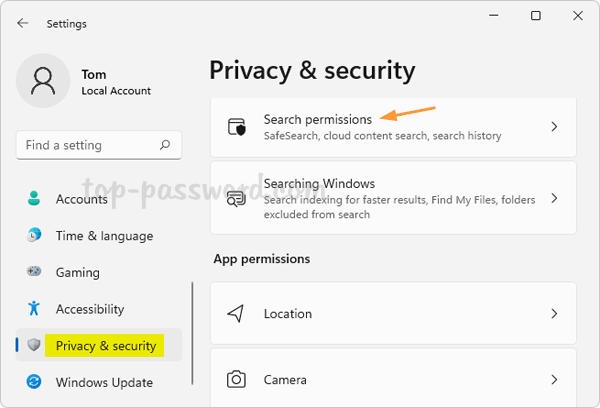
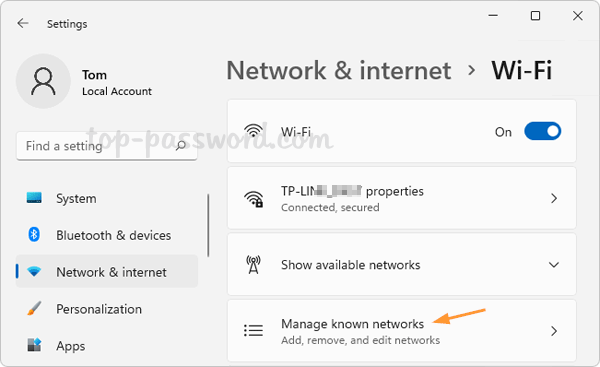
- Press the Windows key + I keyboard combination to launch the Settings app. Click Network & internet on the left menu, and then click Wi-Fi on the right pane.
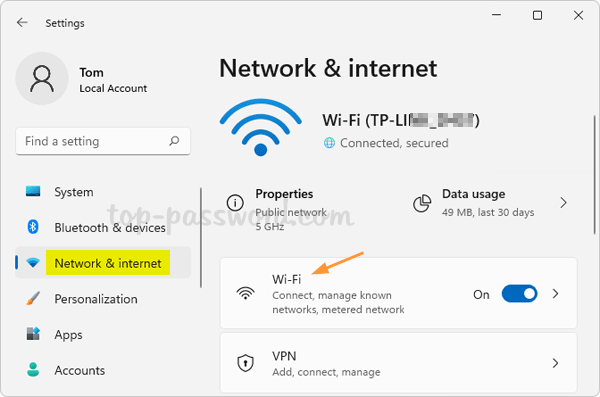
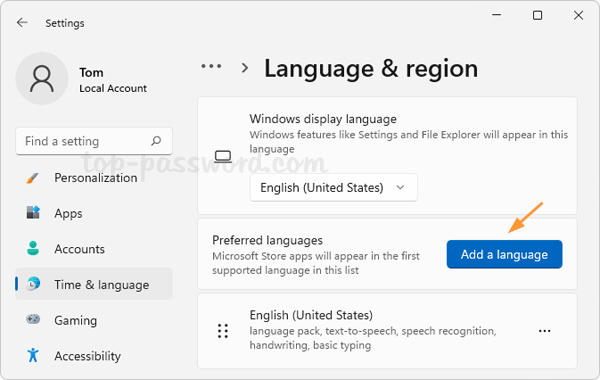
- Click “Manage known networks“.
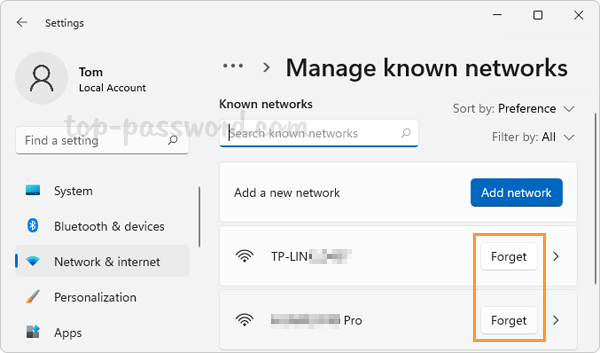
- You can see the full list of all the Wi-Fi networks that Windows 11 has remembered previously. Once you find the Wi-Fi network that you want to remove, click the Forget button next to its name.
Conclusion
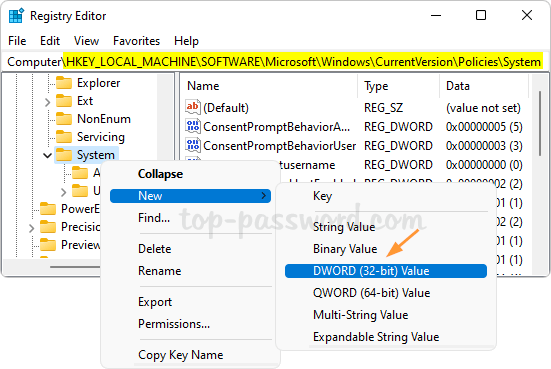
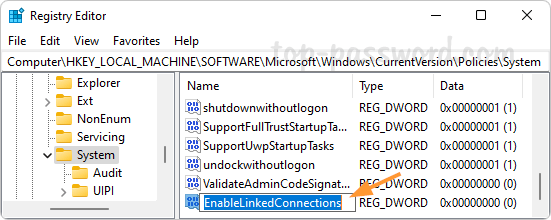
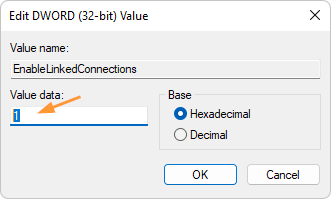
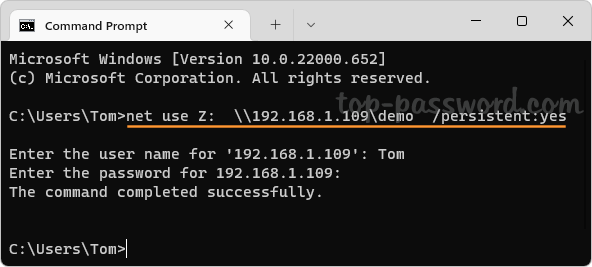
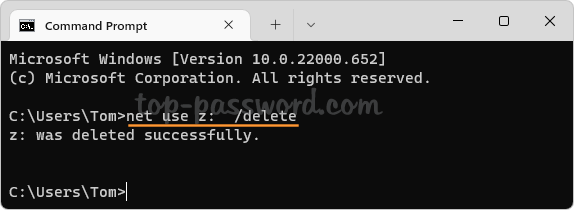
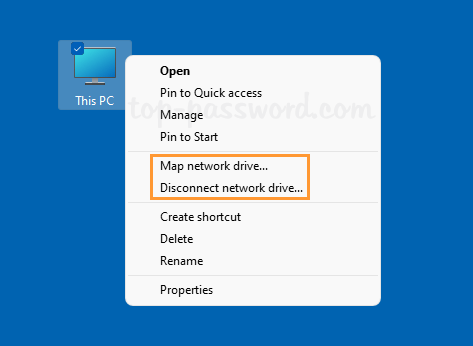
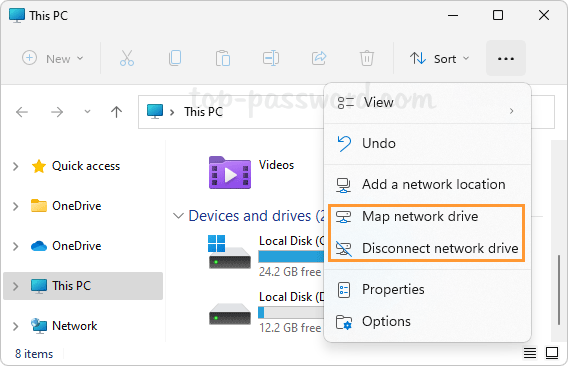
That’s how you can easily forget a Wi-Fi network in Windows 11. You can also remove saved Wi-Fi networks using the other 3 methods: How to Delete Wireless Network Profiles in Windows 11 / 10 / 8 / 7 using system tray, Command Prompt or Registry Editor